What is an SoC? - All About Tech
Hello, Questers!
I hope you guys are having a good day. Tech enthusiasts always specify the processing power and chips when talking about PCs or the latest smartphones. While speaking about processing power and chips is often dense with jargon and abstract-sounding ideas that can feel like brick walls to understanding even basic questions like "What is an SoC ?"

An SoC, or "System on a Chip," is the central component of every modern smartphone. Things like a CPU, a GPU, input and output ports, memory and cache, and more are built into an SoC depending on what its purpose is.
SoC can be explained with an example of the human head; visualise your head as the SoC and your brain, which is located within the head, as the processor. Just like our head integrates many other parts, the SoC, too, contains various components. Many of these components also help take the load off the processor and help it perform more efficiently.
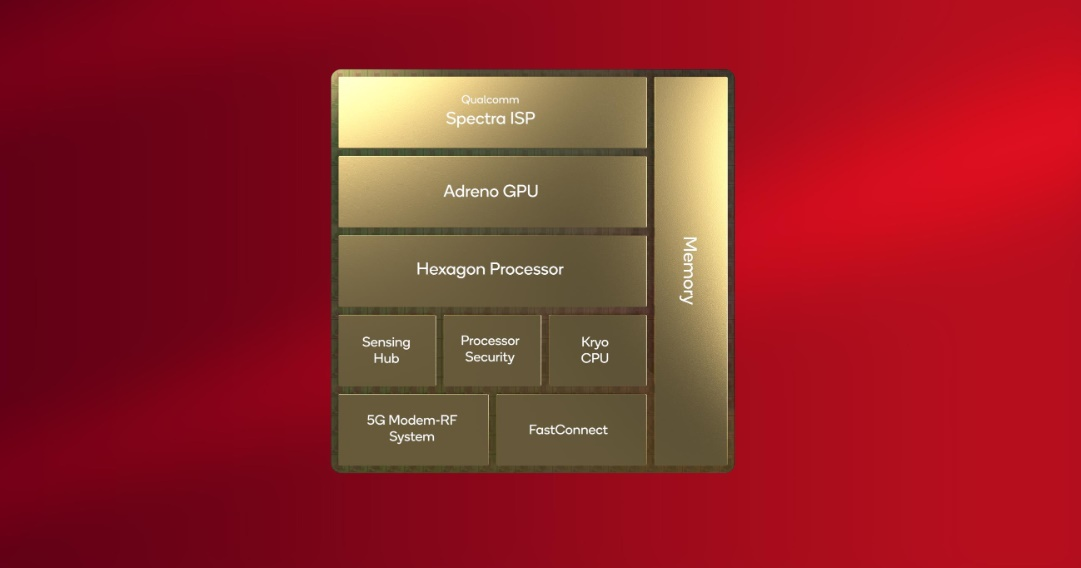
Combining multiple components into a single chip saves on space, cost, and power consumption. The SoC functions as a single unit and is responsible for handling almost every single task you ask your phone to perform, from the Android operating system to detecting when you press the power off button. SoCs connect to other components too, such as cameras, a display, RAM, flash storage, and much more.
Components of an SoC
👉 Central Processing Unit (CPU): The "brains" of the SoC runs most of the code for the Android OS and most of your apps, and its performance is measured in GigaHertz (GHz).
👉 Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): handles graphics-related tasks, such as visualising an app's user interface and 2D/3D gaming.
👉 Image Processing Unit (ISP): converts data from the phone's camera into image and video files.
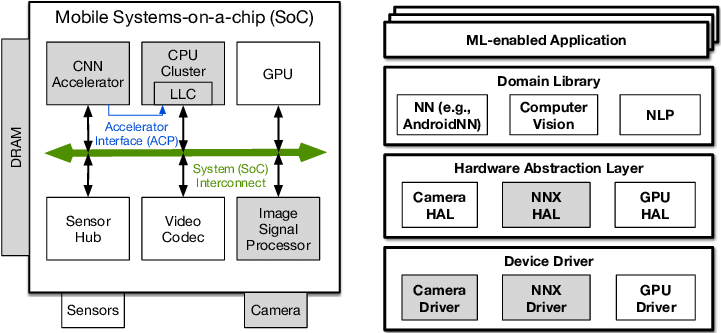
👉 Digital Signal Processor (DSP): handles more mathematically intensive functions than a CPU. Includes decompressing music files and analysing gyroscope sensor data.
👉 Neural Processing Unit (NPU): used in high-end smartphones to accelerate machine learning (AI) tasks. These include offline voice recognition and camera object segmentation.
👉 Video Encoder/Decoder: handles the power-efficient conversion of video files and formats.
👉 Integrated Modems: Convert wireless signals into data your phone understands. Components include 4G LTE, 5G, WiFi, and Bluetooth modems.
What is nm in a SoC?
nm stands for nanometer, a unit of measure for length. In a SoC/CPU, nm is used to measure the size of the transistors that make up the processor. There are billions of transistors in a CPU that perform calculations through electrical signals by switching on and off. 1nm is equal to 0.000000001 metres, which is absolutely minute.
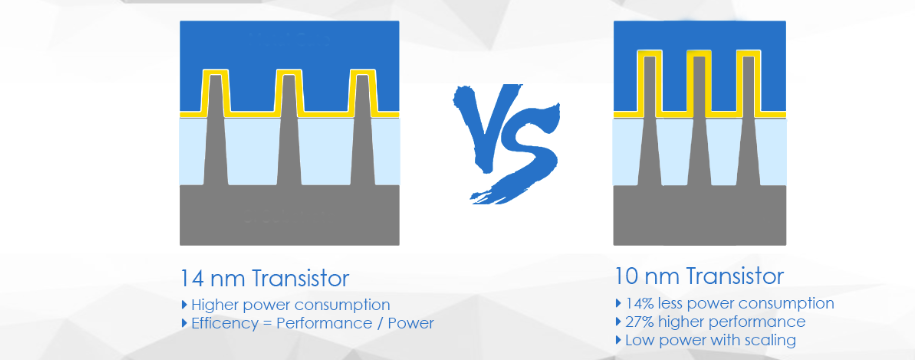
Current flagship SoCs are based on 4-nm manufacturing processes. Mid-range and budget SoCs are typically based on 7, 10, 11, 12, and 14 nm manufacturing processes.
Usually, when you look at the specifications of a smartphone or a PC, you go for the ones with higher numbers. The case with nm is quite the opposite. Lower nm is better for your machine due to the following reasons:
👉 More power-efficient
In order to switch on or off, transistors require power. So, a lower-nm transistor means less power is required for it to work.
👉 Less cooling is required
Relating to the first point, when the transistors in your CPU consume less power, less heat is generated overall. So, your machine requires less cooling to keep working optimally.
👉 Transistors Are Faster
When the transistor size is smaller, there is less distance between them. Less distance means the electric signal will travel faster, improving the overall performance of the CPU.
👉 Transistor density is higher
Lower nm will increase the transistor density of a CPU. A lower-nm processor can fit in more transistors, and more transistors typically translate to more computing power.
➡️ Real-World Examples of Better CPU Performance with Lower nm
Let's consider an example where lower nm makes the overall machine faster. If you compare the iQOO Neo 7 with the Infinix Note 10 Pro, you'll find many similar specifications. For example, both have an octa-core processor and 8 GB of RAM. Both offer 128GB or 256GB internal storage variants. Even their sizes and screen resolutions are almost the same.

So why is the iQOO Neo 7 so much better in terms of performance? Yes, you guessed it. It's the nm of its processor along with the clock speed that make it superior in performance. The iQOO Neo 7 uses a 4nm processor, while the Infinix Note 10 Pro uses a 12nm processor. So, there is a huge difference in the distance between their transistors, making a major difference in terms of efficiency and performance.
This is all about SoC, and what you should focus on is the result of having the right SoC inside your phone, from power-sipping to extreme performance, so that it can handle the tasks you value most. Now, we have a large variety of choices to pick from.
📌 I hope this thread was informative. I will catch you soon with another topic. Do share your thoughts below in the comments section.
Please sign in
Login and share

























