Evolution of Android OS: From 1.0 to Android 13 and Future Android 14

The Android operating system has come a long way since its inception in 2008 with the release of Android 1.0. Developed by Google, Android has revolutionized the mobile industry and has become the most popular operating system worldwide. Over the years, Android has undergone significant changes and improvements, introducing new features, enhancing performance, and expanding compatibility. In this article, we will explore the evolution of Android OS from its initial version to the latest release, Android 13, and also peek into the future with Android 14.
Android 1.0 - Cupcake:
Android 1.0, codenamed Cupcake, marked the birth of the Android OS. It introduced several fundamental features, such as a virtual keyboard, widgets, and the ability to upload videos to YouTube. This version laid the foundation for subsequent updates and set the stage for the rapid growth of Android in the coming years.
Android 2.0 - Eclair:
Released in 2009, Android 2.0, known as Eclair, brought significant improvements to the user experience. It introduced features like multiple account support, HTML5 support in the browser, and Microsoft Exchange support. Eclair also marked the introduction of Google Maps Navigation, a turn-by-turn navigation system, which disrupted the standalone GPS industry.
Android 4.0 - Ice Cream Sandwich:
Ice Cream Sandwich, released in 2011, was a major milestone for Android as it brought a unified user interface design called "Holo." This version focused on providing a consistent experience across different devices. It introduced features like face unlock, resizable widgets, and a revamped notification system. Ice Cream Sandwich also brought improvements in performance and introduced the popular Chrome browser.
Android 5.0 - Lollipop:
Lollipop, released in 2014, brought a significant visual overhaul to the Android OS. It introduced the "Material Design" language, which aimed to provide a more intuitive and visually appealing user interface. Lollipop also focused on improving battery life through a feature called "Project Volta" and introduced support for 64-bit processors.
Android 6.0 - Marshmallow:
Marshmallow, released in 2015, focused on improving user control and security. It introduced features like app permissions, allowing users to grant or revoke specific permissions on an app-by-app basis. Marshmallow also brought improvements in battery life through a feature called "Doze" that reduced background activity when the device was idle.
Android 7.0 - Nougat:
Nougat, released in 2016, aimed to enhance productivity and user experience. It introduced features like split-screen multitasking, direct reply to notifications, and a redesigned quick settings panel. Nougat also introduced Vulkan API for better gaming performance and Daydream, Google's platform for virtual reality.
Android 8.0 - Oreo:
Oreo, released in 2017, focused on speed, performance, and reducing background activity. It introduced features like picture-in-picture mode, notification dots, and improved autofill for easier form filling. Oreo also introduced Project Treble, which aimed to streamline the Android update process by separating the underlying framework from the vendor-specific modifications.
Android 9.0 - Pie:
Pie, released in 2018, emphasized artificial intelligence and machine learning. It introduced features like Adaptive Battery, which used AI to prioritize battery power for frequently used apps. Pie also brought gesture-based navigation, a redesigned app switcher, and a Digital Wellbeing suite that aimed to promote a healthier relationship with smartphones.
Android 10 - A Focus on Privacy and Gesture Navigation:
Released in 2019, Android 10 marked a significant shift for the operating system, introducing a host of new features and enhancements. Privacy became a top priority, with Android 10 offering more control over app permissions and improved location settings. It also introduced a system-wide dark mode, enhancing battery life and reducing eye strain. Additionally, Android 10 brought gesture-based navigation, allowing users to navigate their devices with fluid gestures.
Android 11 - Enhanced Communication and Device Control:
Android 11, launched in 2020, focused on improving communication and device control. It introduced a dedicated conversation section in the notification shade, making it easier to manage and prioritize messages. Android 11 also enhanced device control with the introduction of device and media controls in the power menu. Users could quickly switch between connected devices and control media playback.
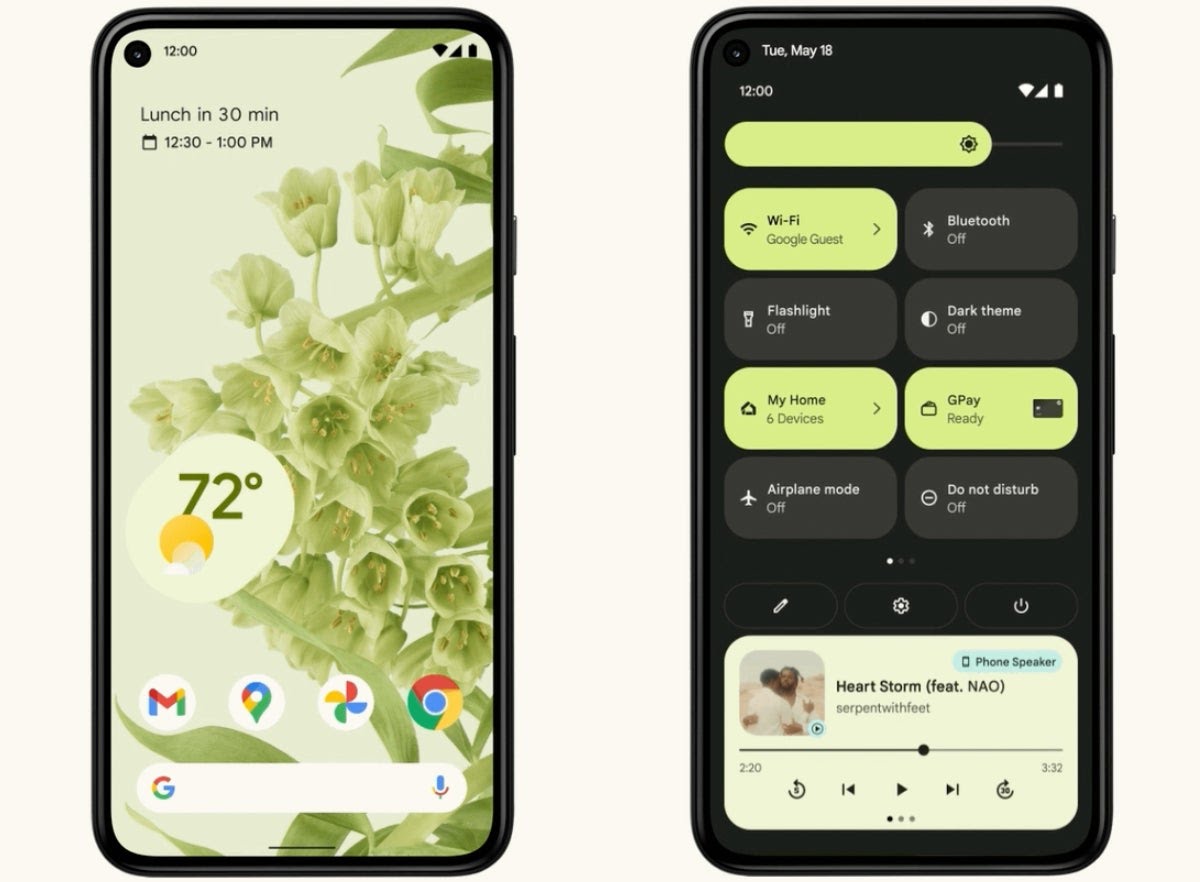
Android 12 - Material You and Privacy Dashboard:
Android 12, released in 2021, brought a major visual overhaul with the introduction of "Material You." This design language allowed for more customization, adapting system colors and themes based on user preferences. Android 12 also introduced a Privacy Dashboard, providing users with an overview of app permissions and data access. It aimed to empower users with greater control over their privacy.

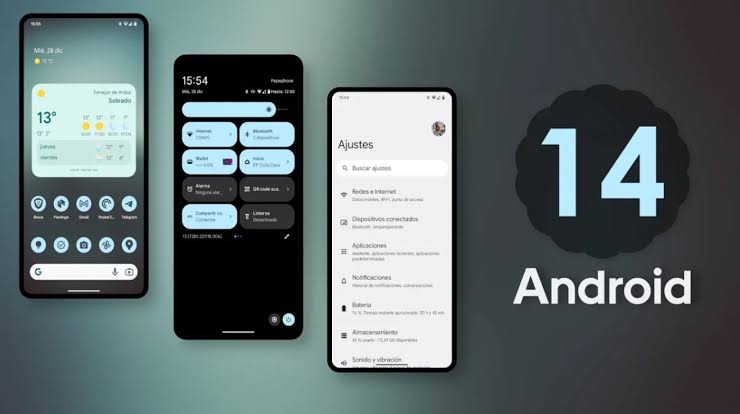
Android 13 - Performance Improvements and Enhanced Accessibility:
The recently released Android 13, in 2022, continues the trend of refining the user experience. It focuses on performance improvements, optimizing system resources, and enhancing battery life. Android 13 also brings advanced privacy features, such as approximate location permissions, allowing users to share only an approximate location instead of precise details. Additionally, accessibility received attention with new features like improved gesture navigation for users with limited dexterity and a built-in Live Caption feature.
The Future of Android 14 - An Exciting Outlook:
While specific details about Android 14 are yet to be revealed, we can anticipate exciting developments based on previous trends and user demands. Google is likely to continue refining the user interface, with potential enhancements in customization options and visual aesthetics. As privacy remains a pressing concern, Android 14 might introduce further privacy-centric features and controls.
In terms of performance, we can expect optimizations to enhance the overall speed, efficiency, and battery life of Android devices. Google may also focus on strengthening device security by introducing additional layers of protection against evolving cyber threats.
As the Android ecosystem expands, integration with other devices and services will likely play a prominent role in Android 14. Seamless connectivity across various devices, improved cross-platform compatibility, and integration with emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and Internet of Things (IoT) could be on the horizon.

Conclusion:
The evolution of the Android operating system from Android 10 to Android 13 showcases the continuous efforts by Google to provide users with enhanced privacy, improved performance, and a more personalized experience. As we eagerly anticipate Android 14, we can anticipate further advancements in privacy, customization, performance, and integration, making the Android OS even more versatile and user-friendly. Android's journey of innovation is far from over, promising exciting possibilities for the future of mobile computing.
Please sign in
Login and share

























