Evolution of Mobile Networks: From 1G to 6G
Evolution of Mobile Networks: From 1G to 6G
In the last few decades, the telecommunications industry has witnessed a remarkable transformation, largely driven by the evolution of mobile networks. The journey from the first generation (1G) to the anticipated sixth generation (6G) has been marked by exponential advancements in technology, enabling faster communication, richer multimedia experiences, and the seamless integration of devices into our daily lives.
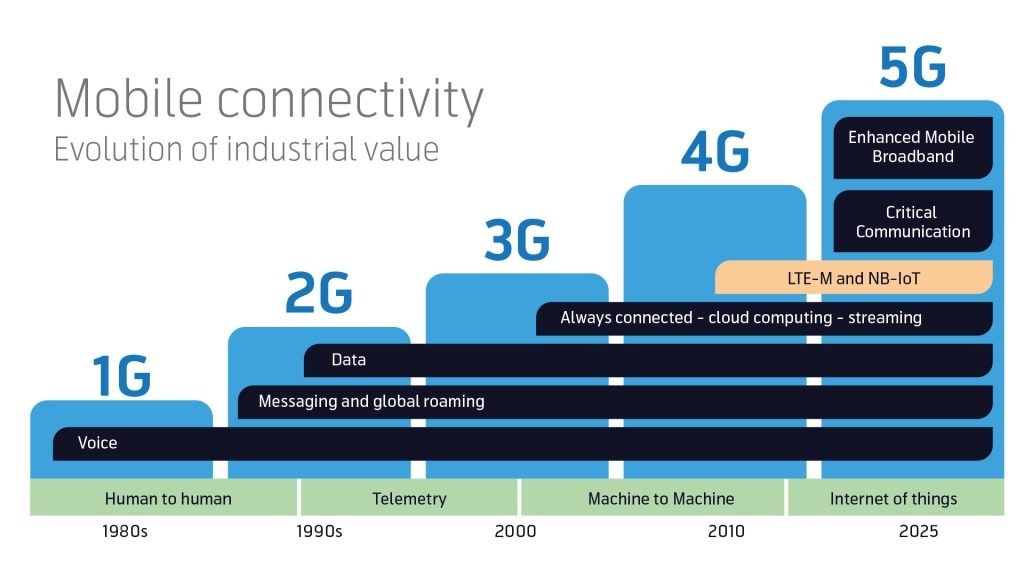
1G: Laying the Foundation
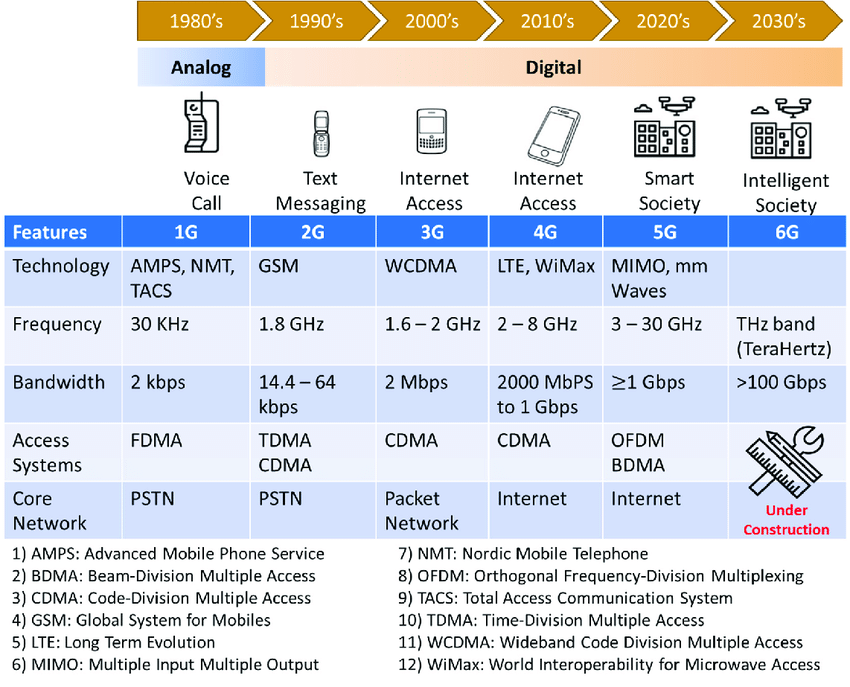
The inception of mobile networks can be traced back to the 1980s with the introduction of 1G technology. First-generation mobile networks were analog and primarily designed for voice communication. These networks provided basic voice calls with a very limited coverage area, low voice quality, and susceptibility to interference. The transition from landline telephony to wireless communication marked a significant shift, despite the limitations of 1G technology.
Internet Speed: 1G networks did not offer internet access as we know it today. They were purely analog and designed primarily for voice calls.
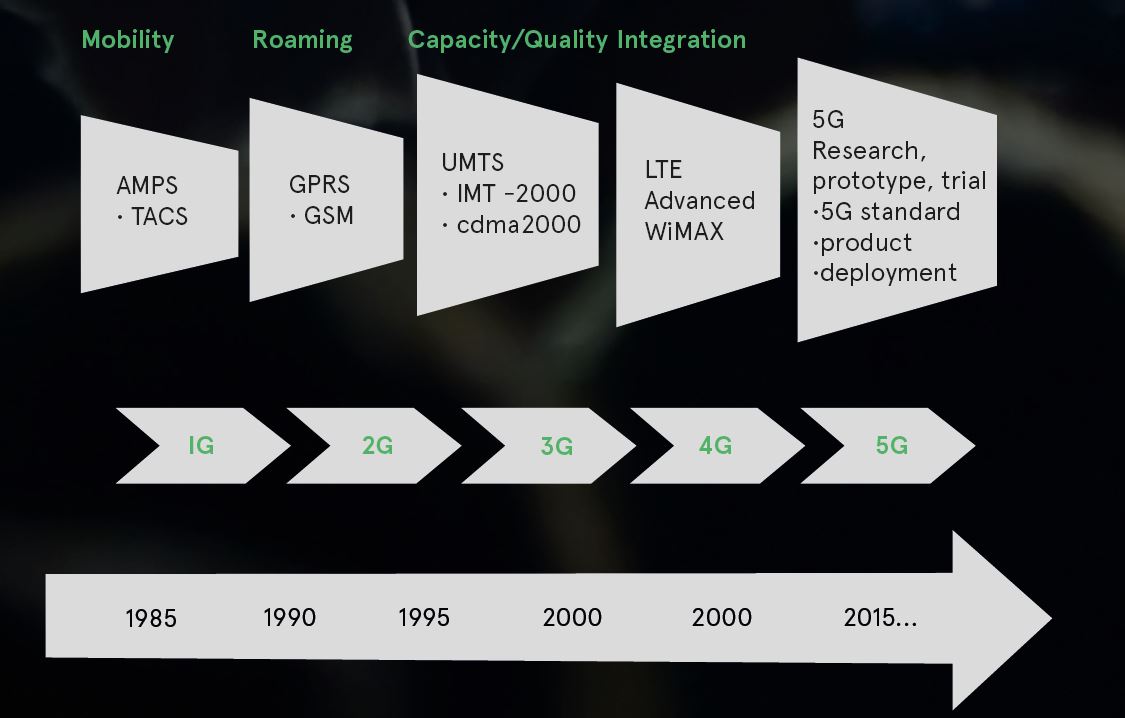
2G: The Digital Revolution
The second generation (2G) emerged in the 1990s, heralding the shift from analog to digital communication. This phase saw the introduction of technologies like GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access). These networks brought about improved voice clarity, text messaging (SMS), and basic data services like email and rudimentary web browsing. The introduction of 2G was a pivotal moment, laying the groundwork for more sophisticated mobile services.
Benefits:
- Digital Communication: 2G introduced digital signals, leading to clearer voice quality and reduced interference.
- Text Messaging: SMS became widely popular, revolutionizing communication beyond voice calls.
- Efficiency: Digital signals allowed for more efficient use of the limited frequency spectrum.
Drawbacks:
- Limited Data Speeds: While 2G enabled basic data services, data speeds were still quite slow for modern demands.
- Limited Data Capacity: 2G struggled to support data-intensive applications due to its limited capacity.
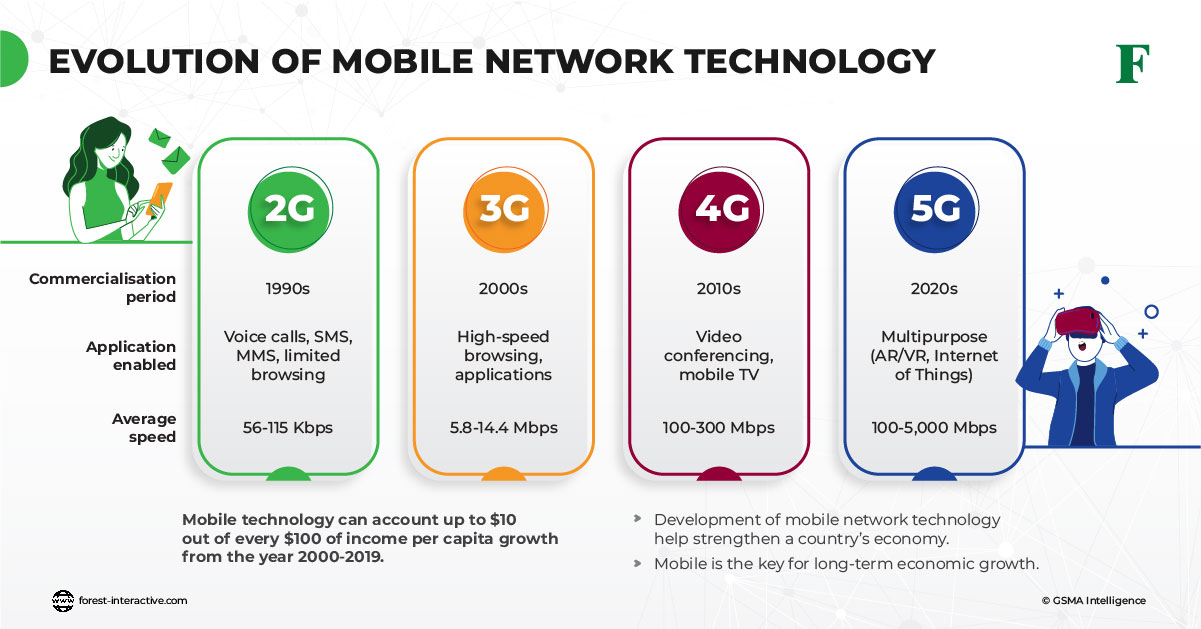
Internet Speed: 2G networks offered data speeds of up to 64 Kbps (kilobits per second), which were sufficient for basic text-based internet services like email and simple web browsing.
3G: The Birth of Mobile Data
The turn of the millennium saw the rise of third-generation (3G) networks, which aimed to revolutionize mobile communication by introducing mobile data services. Technologies like UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) and CDMA2000 enabled faster data transfer rates, paving the way for video calling, mobile internet, and more advanced data applications. Although 3G networks marked a significant advancement, their speeds were still relatively slow for the growing demands of multimedia content.
Benefits:
- Mobile Data: 3G introduced mobile data services, enabling web browsing, email, and basic multimedia.
- Video Calling: Faster data speeds allowed for video calling and conferencing.
- Data Applications: 3G paved the way for mobile apps and basic online services.
Drawbacks:
- Limited Speeds for Multimedia: Despite improvements, 3G was not ideal for seamless streaming of high-quality multimedia content.
- Coverage Challenges: 3G coverage wasn't universal, and rural areas often had limited access.
Internet Speed: 3G networks offered data speeds ranging from 384 Kbps to 2 Mbps (megabits per second), allowing for improved web browsing, email, and basic video streaming.
4G: The Era of Mobile Broadband
With the advent of fourth-generation (4G) networks, mobile communication took a giant leap forward. Introduced in the late 2010s, 4G technologies like LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and WiMAX provided significantly faster data speeds, low latency, and the ability to handle high-definition video streaming, online gaming, and other data-intensive applications. The shift to 4G facilitated the rise of the app economy and transformed how individuals interacted with technology, enabling seamless content consumption and communication on the go.
Benefits:
- High-Speed Data: 4G offered high-speed mobile broadband, enabling smooth HD video streaming and online gaming.
- Low Latency: Reduced latency improved real-time communication and interactive applications.
- App Economy: 4G was crucial for the growth of app-based services and the mobile ecosystem.
Drawbacks:
- Coverage Gaps: While 4G coverage improved, there were still areas with limited or no coverage.
- Infrastructure Requirements: The deployment of 4G required significant infrastructure upgrades, which posed challenges in some regions.
Internet Speed: 4G networks offered data speeds ranging from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps (gigabit per second), allowing for high-quality video streaming, online gaming, and rapid downloads.
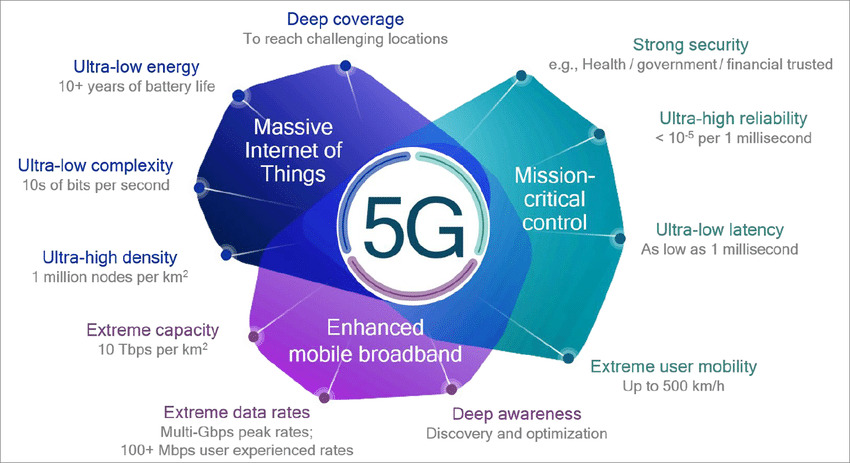
5G: Connecting the Unconnected
The fifth generation (5G) of mobile networks, which began rolling out in the 2020s, was characterized by its promise to interconnect not only people but also machines, objects, and devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. 5G brought about ultra-fast data speeds, remarkably low latency, and the capacity to handle a massive number of connected devices simultaneously. This technology opened doors for augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), remote surgery, autonomous vehicles, and other futuristic applications that depend on instantaneous communication.
Benefits:
- Ultra-Fast Speeds: 5G offered blazing-fast data speeds, reducing download and upload times significantly.
- Low Latency: The near-instantaneous communication enabled applications like remote surgery and real-time VR.
- IoT Integration: 5G's capacity to connect a vast number of devices revolutionized the IoT landscape.
Drawbacks:
- Infrastructure Challenges: 5G requires dense infrastructure deployment due to its use of higher frequencies, which can be costly and time-consuming.
- Signal Range: 5G signals have shorter range compared to previous generations, necessitating more cell towers and infrastructure.
Internet Speed: 5G networks offer data speeds that can range from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps or even higher in some cases, enabling virtually lag-free experiences for applications like VR, AR, and real-time remote control.

6G: Envisioning the Future
As we look ahead to the future, the development of sixth-generation (6G) networks is already underway. While 5G is still being deployed and integrated into various sectors, researchers and technologists are envisioning the possibilities of 6G. The goals for 6G include even faster data speeds, reduced latency to the nanosecond level, ubiquitous connectivity, and the ability to harness terahertz (THz) frequencies for unprecedented performance. 6G aims to empower technologies like holographic communication, advanced AI-driven applications, and a more immersive digital world.
Benefits (anticipated):
- Unprecedented Speeds: 6G aims for data speeds that could exceed 100 times those of 5G.
- Minimal Latency: Near-instant communication could enable applications we can't yet imagine.
- Advanced Technologies: 6G could be the backbone for AI-driven applications, advanced AR/VR, and more.
Drawbacks (anticipated):
- Technical Challenges: Harnessing terahertz frequencies and achieving ultra-low latency presents significant technical hurdles.
- Deployment Complexity: Implementing 6G's advanced technology on a global scale will be complex and expensive.
Internet Speed (anticipated): 6G is expected to offer data speeds that could reach 100 Gbps or more, enabling rapid data exchange for extremely data-intensive applications and immersive experiences.
The evolution of mobile networks from 1G to 6G is a testament to human innovation and the constant quest for improved communication. Each generation has built upon the shortcomings of its predecessor, ushering in new capabilities, services, and experiences that have transformed societies and industries. As we stand on the cusp of the 6G era, it's clear that the future holds even more astonishing possibilities, reshaping how we connect, communicate, and collaborate in ways we can only begin to imagine. While each generation has brought benefits and drawbacks, the overall trajectory has been towards faster, more reliable, and more connected communication systems that have redefined the way we live and work.
Nitin Panwar
Moderator
Please sign in
Login and share

























