Decoding PWM in OLED Phones - Balancing Eye Comfort and Power Efficiency
Pros & Cons of PWM Dimming

Pros of High-Frequency PWM
1. Eye Protection: High-frequency PWM significantly reduces the adverse effects of screen flashes on the human eye compared to lower frequencies.
2. Improved Display: Addresses the poor display quality of low brightness associated with DC dimming, enhancing the overall visual experience.
Cons of High-Frequency PWM:
1. Increased Power Consumption: As the PWM frequency rises, so does the power consumption of the mobile phone, leading to faster battery drain.

EM low-level activation within PWM dimming rapidly toggles screen brightness, leveraging higher frequencies to alleviate eye strain for users. This innovation, however, comes with a cost, as it significantly amplifies power consumption within devices. The nuanced balance between visual comfort and energy efficiency becomes apparent, posing a trade-off inherent to this technological advancement. This method, reliant on the oscillation of brightness states, aims to maintain a consistent display through human visual persistence. Its implementation necessitates careful consideration of PWM frequency to optimize user experience while managing the device's energy demands effectively.
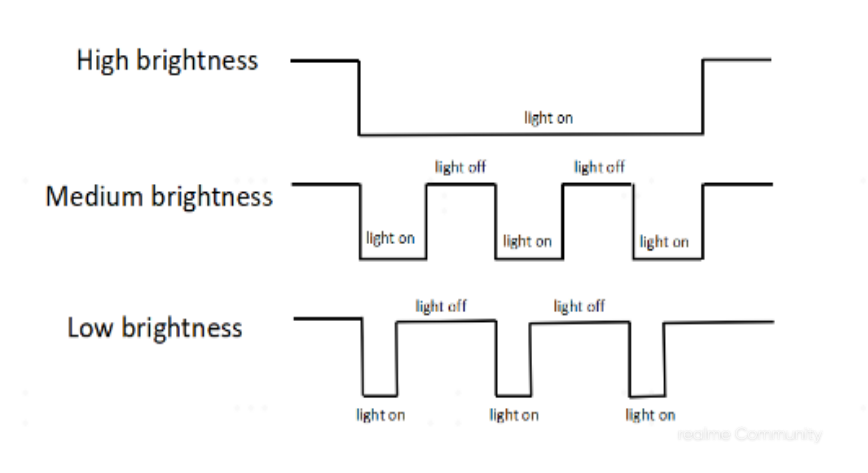
DC dimming involves altering screen brightness by adjusting the power supplied to the screen. While it ensures better color brightness uniformity in high brightness settings, it results in uneven color and brightness in low light environments, causing screen noise or a "rag screen." PWM dimming, on the other hand, utilizes rapid on-off cycles to adjust brightness but can cause stroboscopic issues and eye discomfort at lower frequencies
Conclusion:
High-frequency PWM, operating above 1250 Hz as per IEEE and relevant national standards, offers a balance between eye protection and display quality for OLED screens. According to IEEE requirements and relevant national standards, the harm to human eyes caused by PWM frequency higher than 1250 Hz is low risk. At present, the PWM frequency of OLED mobile phones on the market has reached 2160 Hz or even 3840 Hz, which greatly solves the harm of screen flash to the eyes. Although it effectively mitigates eye strain caused by screen flashes, it simultaneously escalates power consumption, impacting the device's battery life. This advancement in technology signifies a trade-off between enhanced user comfort and increased energy usage in modern mobile devices.
Please sign in
Login and share

























