Let's Learn Mobile Tech In-Depth: #4). Sensors_Part1
Hey iQOO Fam,
In this series, we'll be diving straight into the core components & Tech that is inside in our daily drive, discussing the latest advancements and what's coming next.
Let's get into the first three sensors in this thread as part1:
Accelerometer, Gyroscope and Magnetometer
To understand their working principles, applications, and the tech behind them. These sensors are the backbone of your smartphone's interaction with the physical world, and their engineering is nothing short of fascinating.
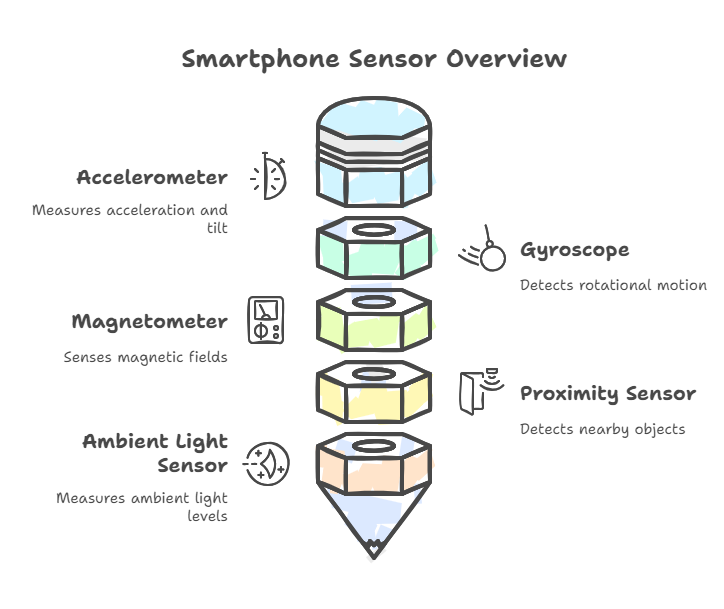
1. Accelerometer: The Motion Detector
How It Works:
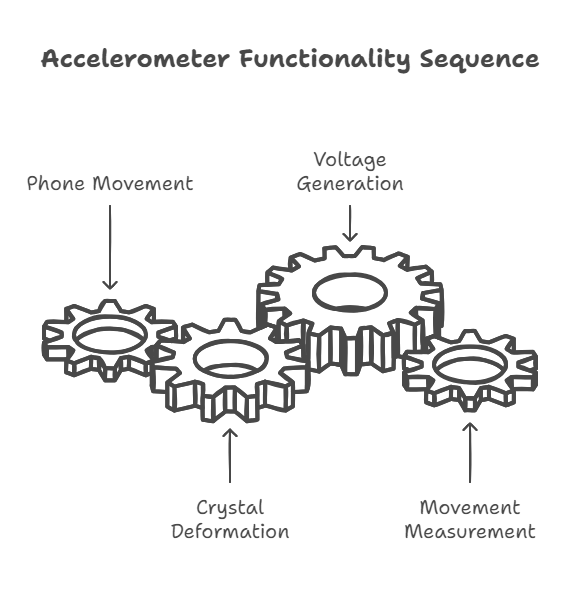
- The accelerometer measures acceleration forces (change in velocity) in three dimensions: X (left-right), Y (forward-backward), and Z (up-down).
- It uses microscopic crystal structures that generate a voltage when subjected to mechanical stress (piezoelectric effect).
- When your phone moves, these crystals deform, and the resulting voltage is measured to determine the direction and intensity of the movement.
Key Applications:
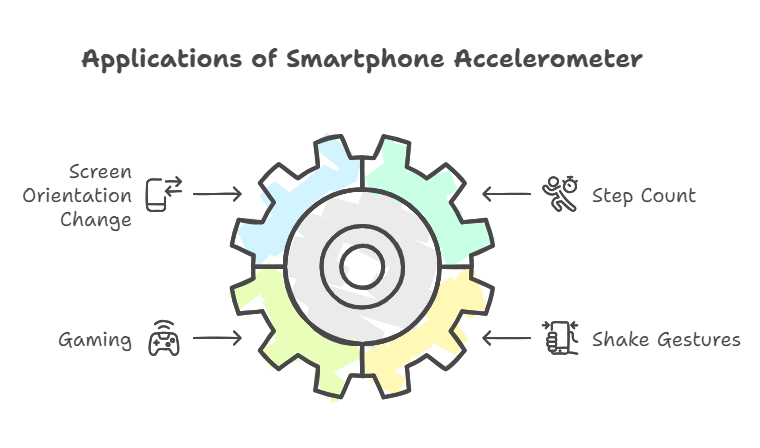
- Screen Orientation Change: For automatically switching in and out of Portrait/Landscape views
- Step Count: Measured and records repetitive-motion activity, like turning and twisting while on the way
- Games:Provides you with motion sensing abilities (think tilt-to-steer racing apps).
- Shake gestures: allows to make your phone act to undo the application or open to refresh
Modern accelerometers are based on MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology, which integrates mechanical and electrical components on a microscopic scale. This makes them incredibly small, efficient, and accurate.
2. Gyroscope: The Spin Master
How It Works:
The gyroscope measures angular velocity—how fast your phone is rotating around an axis.
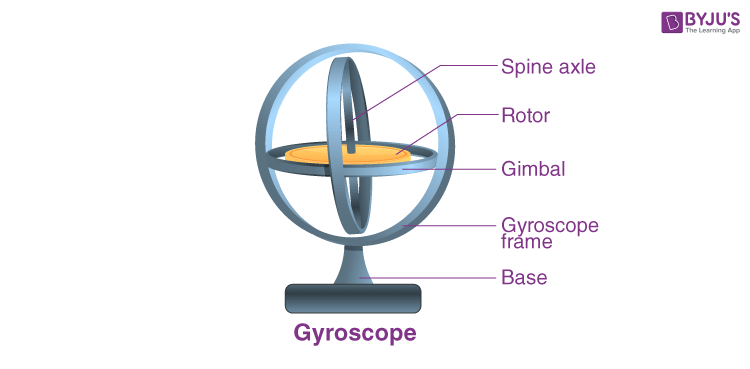
It's based on the Coriolis effect: a vibrating mass inside the sensor deflects when the phone rotates, and this deflection is measured to determine the rate of rotation. Like the accelerometer, it works on three axes (X, Y, Z).
Key Applications:
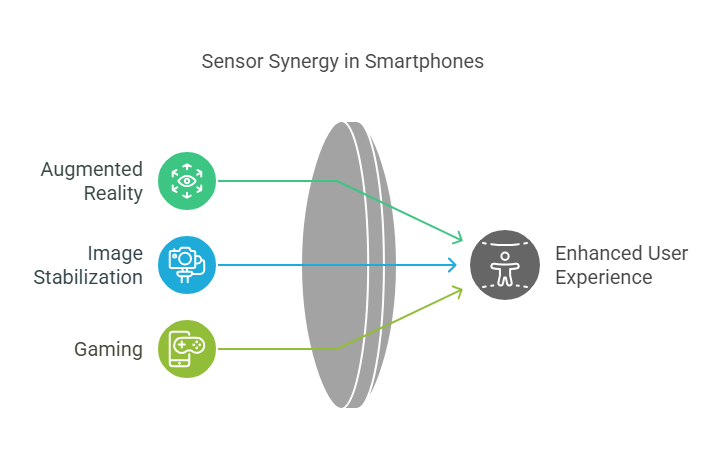
Augmented Reality (AR): Tracks precise movements for immersive AR experiences.
Image Stabilization:Helps cameras compensate for handshakes during photos and videos.
Gaming: Enhances motion controls by detecting rotational movements (e.g., aiming in shooting games).
Pro Tip:
The gyroscope works in tandem with the accelerometer to provide a complete picture of your phone's motion. This combination is called sensor fusion, and it's why your phone can detect complex movements with such accuracy.
3. Magnetometer: The Digital Compass
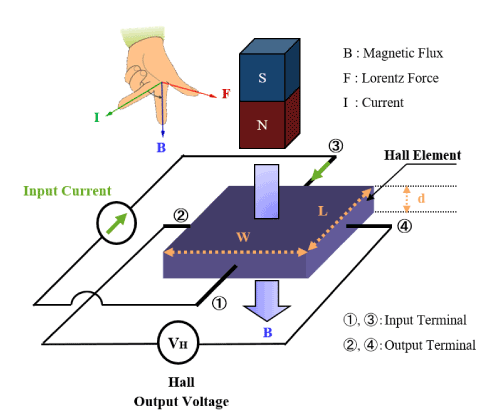
How It Works:
This component detects the earth's magnetic fields through the use of a Hall-effect sensor or a magnetoresistive element. Its operational strength and direction will allow your phone to know where it is in terms of magnetic north.
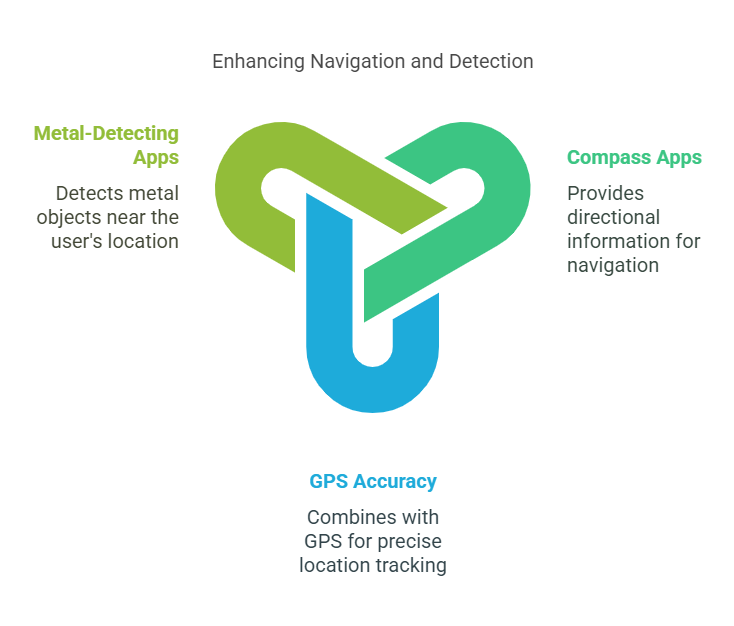
Key Applications:
- Has useful directional information for compass apps
- With GPS combination, it also enhances the location accuracy
- Even powers metal-detecting apps, which can sense metal objects close to your position
Cool Use Case:
The magnetometer is also used in augmented reality apps for aligning virtual objects to the real world. For example, it helps AR apps place virtual furniture in your room accurately.
# Do follow me for more quality content on Tech and Photography.
Signing off,
Balaji Murapaka
iQOO Ranger_South Zone

Please sign in
Login and share

























